在VSCode中给获取到的canvas对象增加代码提示
js
// 在获取 canvas 对象的前一行,加上下面这行注释,即可获得代码提示
/** @type {HTMLCanvasElement} */
const cvs = document.querySelector('canvas')canvas清晰度问题
TIP
原始尺寸 = 样式尺寸 * 缩放倍率 , 只要能保持这个等式成立,图片就不会模糊
eval的替代方案
将字符串解析为表达式并计算结果
js
// 注意return后面要留有一个空格
const result = new Function('return ' + 'Math.random() > 0.5 ? 1 : 0')()
console.log(result)将字符串解析为JS代码并执行
js
new Function('console.log(Math.random())')()动态加载并执行JS代码
js
const script = document.createElement('script')
script.textContent = 'console.log(Math.random())'
document.head.appendChild(script)编程语言对小数运算不精确的问题根源
0.3 - 0.2 === 0.1的判断结果为false,出现这个问题的原因是小数运算的精度丢失。至于为什么会精度丢失,那就要来了解小数转换二进制的过程了
TIP
小数转换二进制口诀:「乘 2 取整,顺序排列」
示例1
js
0.125 => 01
0.125 * 2 = 0.5 0
0.5 * 2 = 1.0 1
0.0 结束示例2
js
0.2 => 00110011...
0.2 * 2 = 0.4 0
0.4 * 2 = 0.8 0
0.8 * 2 = 1.6 1
0.6 * 2 = 1.2 1
0.2 * 2 = 0.4 0
... 无限循环异或运算求数组中只出现一次的元素
^:按位异或,相同取0,不相同取1
异或运算有以下特点
- 满足交换律:
a^b^c = c^a^b - 两个相同的数字异或运算一定等于零:
a^a === 0 - 零和任意数字进行异或运算一定等于它自身:
0^a === a
通过这三个特点,就有以下思路:a^b^c^a^c转换为a^a^c^c^b转换为0^0^b转换为0^b最后得到b
js
const arr = [1, 1, 2, 3, 4, 2, 5, 6, 4, 5, 7, 6]
arr.reduce((a, b) => a ^ b, 0) // 得到 4普通函数转成柯里化
js
function createCurry(fn, args) {
args = args || []
const length = fn.length
return function () {
const newArgs = args.concat(Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments))
if (newArgs.length < length) {
return curry.call(this, fn, newArgs)
} else {
return fn.apply(this, newArgs)
}
}
}对象的键值只能是String和Symbol类型
来看一道阿里的技术面试题,此题考察的主要是xx.toString():
js
const a = {},
b = { key: 'b' },
c = { key: 'c' }
a[b] = 123 // 等价于 a['[object Object]'] = 123
a[c] = 456 // 等价于 a['[object Object]'] = 456
console.log(a[b]) // 输出 456JS 中的==隐式转换规则
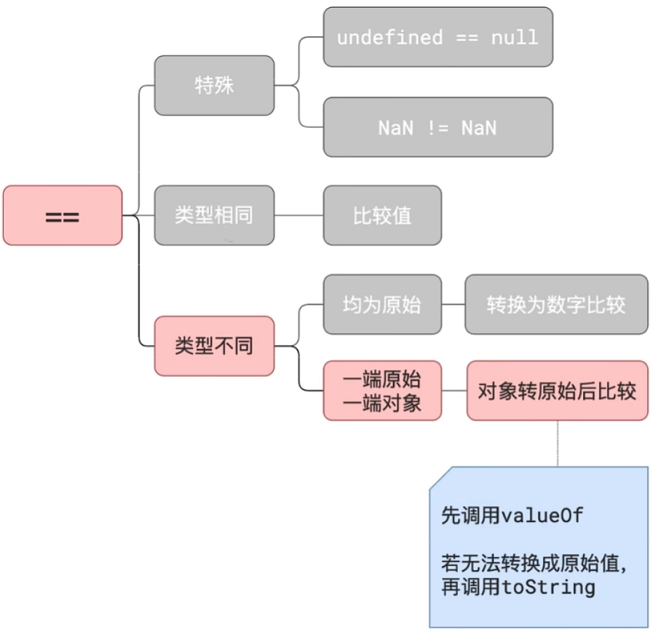
js
const a = ?; // ? 位置要怎么写才能输出 true
console.log(a == 1 && a == 2 && a == 3);js
const a = {
n: 1,
valueOf: function () {
return this.n++
},
}请求队列
js
const handleQueue = (
maxNum = 6 // 最大并发数
) => {
const requestQueue = () => {
const queue = [] // 请求队列
let current = 0 // 当前请求了多少条
const dequeue = () => {
while (current < maxNum && queue.length) {
current++
const currentPromise = queue.shift() // 出列
currentPromise().finally(() => {
current--
dequeue()
})
}
}
return (promise) => {
queue.push(promise) // 入列
dequeue()
}
}
return requestQueue()
}
// 使用示例
for (let i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
handleQueue()(() => Promise.resolve(i).then((res) => console.log(res)))
}计算超出隐藏的单行文本实际宽度
js
function getStyles(elem, prop) {
if (window.getComputedStyle) {
if (prop) {
return window.getComputedStyle(elem, null)[prop]
} else {
return window.getComputedStyle(elem, null)
}
} else {
if (prop) {
return elem.currentStyle[prop]
} else {
return elem.currentStyle
}
}
}
function showRealProp(elem, ...prop) {
if (!elem) throw new Error('dom 节点不能为空')
// 如果属性值为空 则退出
if (prop.length === 0) return
// 真正的width
let realProp = {}
// 克隆dom
const cpNode = elem.cloneNode(true)
// 重置style样式
cpNode.setAttribute(
'style',
'display: inline-block;height: 0;visibility: hidden;font-size: 14px;font-family: Helvetica, "Microsoft Yahei"'
)
// 将dom添加到body后面,如果不添加 下面无法计算盒子的宽度
document.body.appendChild(cpNode)
prop.forEach((item) => {
if (!item) return
// 获取真正属性的styles值
realProp[item] = getStyles(cpNode)[item]
})
// 计算完成后移除该dom节点
document.body.removeChild(cpNode)
return realProp
}
// 使用示例
const elem = document.getElementById('test')
showRealProp(elem, ...['width', 'min-width'])计算localStorage的已使用容量
js
/** @description 计算字符串的字节数 */
function calculateUtf8ByteSize(str) {
// 非字符串 不作计算
if (typeof str !== 'string') 0
// 定义变量,用于累加字节数
let byteCount = 0
// 遍历字符串中的每个字符
for (let i = 0, len = str.length; i < len; i++) {
// 获取当前字符的Unicode码
const charCode = str.charCodeAt(i)
// 根据字符的Unicode码,计算其占用的字节数
if (charCode <= 0x007f) {
byteCount += 1 // 在000000-00007F之间的字符(如字母),占用1个字节
} else if (charCode <= 0x07ff) {
byteCount += 2 // 在000080-0007FF之间的字符(如中文),占用2个字节
} else if (charCode <= 0xffff) {
byteCount += 3 // 000800-00FFFF之间的字符(如中文),占用3个字节
} else if (charCode <= 0x10ffff) {
byteCount += 4 // 010000-10FFFF之间的字符(如表情),占用4个字节
} else {
console.log('该字符超出Unicode编码范围')
}
}
return byteCount
}
/** @description 计算localStorage已使用的容量 */
const computedUsed = () => {
let cacheLen = 0
// 遍历所有key
for (const key in localStorage) {
// 拿到非原型key
if (Object.hasOwnProperty.call(localStorage, key)) {
// 累加缓存的字符串长度
cacheLen += localStorage.getItem(key)
}
}
// 计算缓存字符串所占字节数,并转换为KB
return (calculateUtf8ByteSize(cacheLen) / 1024).toFixed(2)
}一维数组节点数据找出每个节点的所有后代节点
ts
function findChildren<T = any>(list: any[], pid: string[], pidName = 'pid', onlyId = true): T[] {
let res = list.filter(r => pid.includes(r[pidName]))
if (res.length < 1) return []
if (onlyId) {
res = res.map(e => e.id)
return res.concat(findChildren(list, res, pidName, onlyId))
} else {
return res.concat(findChildren(list, res.map(e => e.id), pidName, onlyId))
}
}需要包含自己时
ts
function findMeAndChildren<T = any>(list: any[], me: string[], pidName = 'pid', onlyId = true): T[] {
let res = [], stack = list.filter(r => me.includes(r.id))
if (onlyId) {
stack = stack.map(e => e.id)
}
while (stack.length) {
res = res.concat(stack)
if (onlyId) {
stack = list.filter(r => stack.includes(r[pidName])).map(e => e.id)
} else {
const pds = stack.map(r => r.id)
stack = list.filter(r => pds.includes(r[pidName]))
}
}
return res
}