⚡ 记一次开发 VitePress 代码演示功能插件的经历
此插件项目是一个使用pnpm+workspace+changesets构建的单仓库多项目的monorepo工程
涉及到的核心技术有
- Vite虚拟模块
- 手动管理HMR热更新
unified+remark解析markdownmarkdown-it自定义渲染
实现原理:利用 Vite 插件的transform钩子读取 markdown 内容,使用 unified+remark 解析出自定义 markdown 容器中的代码块,然后将代码块转换为虚拟模块,最后是使用markdown-it对虚拟模块进行自定义渲染
相关文档
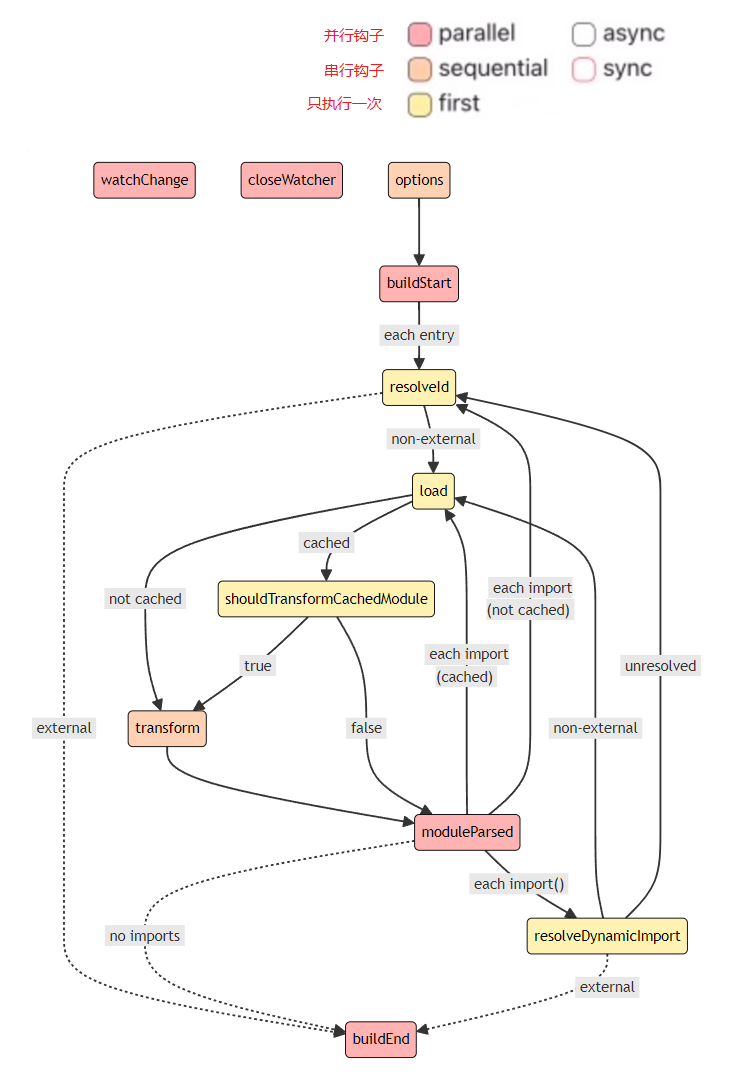
Rollup钩子生命周期
由于 Vite 的插件钩子函数扩展自 Rollup,所以在开始构建项目前,先来看一看 Rollup 的钩子生命周期
async:钩子还可以返回解析为相同类型值的 Promise; 否则,该钩子标记为syncfirst:如果多个插件实现此钩子,则钩子将按顺序运行,直到钩子返回null或undefined以外的值sequential:如果多个插件实现了此钩子,则所有插件都将按照指定的插件顺序运行。如果某个钩子是async,则此类后续钩子将等待,直到当前钩子被解析parallel:如果多个插件实现了此钩子,则所有插件都将按照指定的插件顺序运行。 如果一个钩子是async,则后续的此类钩子将并行运行,而不等待当前的钩子
项目初始化
# 创建项目的根目录
mkdir code-preview && cd code-preview
git init
touch .gitignore
touch .editorconfig
# 示例项目的目录
mkdir docs
# 插件项目目录
mkdir packages/plugin -p
# 演示代码运行所需的容器组件项目
mkdir packages/containerdist
node_modules
docs/.vitepress/cache
docs/.vitepress/dist
.DS_Store
# Logs
logs
*.log
npm-debug.log*
yarn-debug.log*
yarn-error.log*
# Windows shortcuts
*.lnk# http://editorconfig.org
root = true
[*]
indent_style = space
indent_size = 2
end_of_line = lf
charset = utf-8
trim_trailing_whitespace = true
insert_final_newline = true
[*.md]
trim_trailing_whitespace = false
[Makefile]
indent_style = tabpnpm初始化
pnpm init
# 声明工作空间
touch pnpm-workspace.yaml编辑pnpm-workspace.yaml,把上面创建的几个目录添加进去
packages:
- 'docs'
- 'packages/*'接着再编辑package.json,把主项目的名称改为vitepress-code-preview,以及添加如下内容
{
"name": "vitepress-code-preview",
// ...
"workspaces": ["docs", "packages/*"],
"scripts": {
// 表示此项目只允许使用 pnpm
"preinstall": "npx only-allow pnpm"
},
// 包管理器的版本根据自己的情况修改
"packageManager": "pnpm@8.10.0",
"engines": {
"node": ">= 16"
}
}TS环境初始化
因为当前已经转变为workspace工作空间,所以在主项目下安装依赖时需要加一个-w参数
pnpm add -wD typescript @types/node
npx tsc --init{
"compilerOptions": {
"module": "esnext",
"target": "esnext",
"jsx": "preserve",
"moduleResolution": "node",
"strict": true,
"sourceMap": true,
"allowJs": true,
"declaration": true,
"skipLibCheck": true,
"resolveJsonModule": true,
"noUnusedLocals": true,
"strictNullChecks": true,
"esModuleInterop": true,
"forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true
},
"exclude": ["dist", "node_modules"]
}ESLint初始化
由于 ESLint 的问题,无法传递-w参数给 pnpm 会导致初始化时依赖安装失败,所以改成手动安装相关依赖。当然你也可以先进行 ESLint 的初始化,然后再将项目改为workspace工作空间。
npx eslint --init
pnpm add -wD eslint @typescript-eslint/parser @typescript-eslint/eslint-plugin eslint-plugin-vuePrettier初始化
pnpm add -wD prettier eslint-config-prettier eslint-plugin-prettier
touch .prettierrc{
"$schema": "https://json.schemastore.org/prettierrc",
"semi": false,
"tabWidth": 2,
"singleQuote": true,
"printWidth": 100,
"trailingComma": "es5"
}整合ESLint和Prettier
查看
module.exports = {
root: true,
env: {
browser: true,
es2021: true,
node: true,
},
extends: [
'eslint:recommended',
'plugin:@typescript-eslint/recommended',
'plugin:vue/vue3-essential',
'prettier',
'prettier/@typescript-eslint',
],
overrides: [
{
env: {
node: true,
},
files: ['.eslintrc.{js,cjs}'],
parserOptions: {
sourceType: 'script',
},
},
],
parserOptions: {
ecmaVersion: 'latest',
parser: '@typescript-eslint/parser',
sourceType: 'module',
},
plugins: ['@typescript-eslint', 'vue'],
rules: {
complexity: ['error', 10],
'prettier/prettier': 'error',
'no-console': process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' ? 'warn' : 'off',
'no-debugger': process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' ? 'warn' : 'off',
},
}docs示例项目配置
进入docs目录,在里面也进行 pnpm 的初始化,然后把docs下的package.json的name字段值设置为code-preview-example,表示此子项目的名称叫做code-preview-example
cd docs
pnpm init{
"name": "code-preview-example",
// ...
"type": "module",
"peerDependencies": {
"vue": "^3.3.0"
},
"packageManager": "pnpm@8.10.0",
"engines": {
"node": ">= 16"
}
}接着再开始安装 VitePress
⚡ 提示
给子项目安装依赖时,需要使用--filter参数,参数的后面可以指定子项目的目录,也可以指定子项目的名称(就是package.json的name字段值),或者也可以直接进入子项目的目录内执行安装
pnpm add -D vitepress --filter ./docs
pnpm vitepress init
TS配置
新建docs/tsconfig.json,填入如下配置
{
"extends": "../tsconfig.json",
"compilerOptions": {
"paths": {
"~/*": ["./.vitepress/*"]
}
},
"include": ["**/*"],
"exclude": ["node_modules", "dist", ".vitepress/cache"]
}安装Vite
pnpm add -D vite @vitejs/plugin-vue-jsx --filter ./docs新建docs/vite.config.ts
import { defineConfig } from 'vite'
import vueJsx from '@vitejs/plugin-vue-jsx'
export default defineConfig({
plugins: [vueJsx()],
})然后执行pnpm docs:dev试试,不出意外的话,应该可以看到 VitePress 启动成功了
我们继续配置其他子项目
container项目配置
进入packages/container目录,新建tsconfig.json,填入如下配置
{
"extends": "../../tsconfig.json",
"include": ["**/*.vue", "**/*.ts", "**/*.d.ts"]
}同样的,这里也要进行 pnpm 的初始化,但这回是使用 npm(因为pnpm目前不支持--scope参数),并且加上--scope参数表明这是一个带命名空间的包
npm init --scope=@vitepress-code-preview接着再手动修改一下package.json
{
"name": "@vitepress-code-preview/container",
// ...
"type": "module",
"peerDependencies": {
"vue": "^3.3.0"
},
"packageManager": "pnpm@8.10.0",
"engines": {
"node": ">= 16"
}
}plugin项目配置
同样的,进入packages/plugin目录,新建tsconfig.json,填入如下配置
{
"extends": "../../tsconfig.json",
"include": ["**/*.ts", "**/*.d.ts"]
}接着使用 npm 初始化一下,并加上--scope参数
npm init --scope=@vitepress-code-preview老样子,手动修改一下package.json
{
"name": "@vitepress-code-preview/plugin",
// ...
"type": "module",
"packageManager": "pnpm@8.10.0",
"engines": {
"node": ">= 16"
}
}⚡ 到这里,项目的所有基础配置就完成了,接下来开始插件逻辑的开发讲解
container项目开发
先来把示例代码运行所需的容器组件给开发了,就和平时开发先做好静态页面差不多
安装一下基础依赖
pnpm add vue --filter ./packages/container
pnpm add -D vite vitepress @vitejs/plugin-vue-jsx @vitejs/plugin-vue --filter ./packages/container样式
新建packages/container/style/index.css,把需要用到的 VitePress 的 css 变量包装一下,不合适的情况再自己新增
查看
:root {
--preview-white: var(--vp-c-white);
--preview-black: var(--vp-c-black);
--preview-bg: var(--vp-c-bg);
--preview-green-3: var(--vp-c-green-3);
--preview-soft: var(--vp-c-bg-soft);
--preview-mute: var(--vp-c-bg-mute);
--preview-border: rgb(240, 240, 240);
--preview-divider: var(--vp-c-divider);
--preview-text-1: var(--vp-c-text-1);
--preview-text-2: var(--vp-c-text-2);
--preview-text-3: var(--vp-c-text-3);
--preview-text-4: var(--vp-c-text-4);
--preview-code-block-bg: #343030;
--preview-primary-color: var(--vp-c-brand);
}
.dark:root {
--preview-white: var(--vp-c-white);
--preview-black: var(--vp-c-black);
--preview-bg: var(--vp-c-bg);
--preview-green-3: var(--vp-c-green-3);
--preview-soft: var(--vp-c-bg-soft);
--preview-mute: var(--vp-c-bg-mute);
--preview-border: rgb(240, 240, 240, 0.1);
--preview-divider: var(--vp-c-divider);
--preview-text-1: var(--vp-c-text-1);
--preview-text-2: var(--vp-c-text-2);
--preview-text-3: var(--vp-c-text-3);
--preview-text-4: var(--vp-c-text-4);
--preview-code-block-bg: #282626;
--preview-primary-color: var(--vp-c-brand);
}悬浮提示组件
此组件的作用是:当鼠标悬浮在容器组件的一些操作按钮上时会出现气泡提示框,它使用到社区一个有名的包:@floating-ui 的 Vue 版本,所以先安装一下
pnpm add @floating-ui/vue --filter ./packages/container新建packages/container/components/Tooltip.vue,具体代码如下
查看
<template>
<div :class="$style['example-tooltip']">
<div ref="reference" v-on="componentProps">
<slot />
</div>
<div ref="floating" v-show="showFloating" :class="[$style['example-tooltip-content']]">
{{ content }}
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref, defineProps } from 'vue'
import {
offset,
flip,
shift,
computePosition,
Placement,
ReferenceElement,
FloatingElement,
} from '@floating-ui/vue'
defineOptions({
name: 'Tooltip',
})
const props = defineProps<{ placement: Placement; content: string }>()
const reference = ref<ReferenceElement>()
const floating = ref<FloatingElement>()
const showFloating = ref(false)
const update = () => {
computePosition(reference.value!, floating.value!, {
placement: props.placement,
middleware: [offset(10), flip(), shift()],
}).then(({ x, y }) => {
Object.assign(floating.value!.style, {
left: 0,
top: 0,
transform: `translate(${x}px, ${y}px)`,
willChange: 'transform',
pointerEvents: 'none',
})
})
}
const showTooltip = () => {
showFloating.value = true
update()
}
const hideTooltip = () => {
showFloating.value = false
}
const componentProps = {
mouseenter: showTooltip,
mouseleave: hideTooltip,
focus: showTooltip,
blur: hideTooltip,
}
</script>
<style module>
.example-tooltip {
position: relative;
}
.example-tooltip-content {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
z-index: 1;
width: max-content;
min-width: 10px;
padding: 5px 10px;
font-size: 12px;
line-height: 20px;
border-radius: 4px;
word-wrap: break-word;
inset: 0 auto auto 0;
color: var(--preview-white);
background: #303133;
border: 1px solid var(--preview-border);
}
.dark .example-tooltip-content {
color: var(--preview-black);
background: #e5eaf3;
border: 1px solid var(--preview-border);
}
</style>手风琴组件
此组件是用来折叠隐藏示例组件的源码,需要查看的时候点击按钮将其展开,实现逻辑是我从 Element-Plus 那里扒出来的
这个手风琴组件还用到一个 hooks,作用是生成 BEM 格式的 css 类名
- 新建
packages/container/hooks/useNamespace.ts - 新建
packages/container/components/CollapseTransition.vue - 新建
packages/container/style/transition.css - 记得在
packages/container/style/index.css中导入transition.css
查看
// 从element-plus 抄来的, https://github.com/element-plus/element-plus/blob/dev/packages/hooks/use-namespace/index.ts
import { computed, getCurrentInstance, inject, ref, unref } from 'vue'
import type { InjectionKey, Ref } from 'vue'
export const defaultNamespace = 'el'
const statePrefix = 'is-'
const _bem = (
namespace: string,
block: string,
blockSuffix: string,
element: string,
modifier: string
) => {
let cls = `${namespace}-${block}`
if (blockSuffix) {
cls += `-${blockSuffix}`
}
if (element) {
cls += `__${element}`
}
if (modifier) {
cls += `--${modifier}`
}
return cls
}
export const namespaceContextKey: InjectionKey<Ref<string | undefined>> =
Symbol('namespaceContextKey')
export const useGetDerivedNamespace = (namespaceOverrides?: Ref<string | undefined>) => {
const derivedNamespace =
namespaceOverrides ||
(getCurrentInstance()
? inject(namespaceContextKey, ref(defaultNamespace))
: ref(defaultNamespace))
const namespace = computed(() => {
return unref(derivedNamespace) || defaultNamespace
})
return namespace
}
export const useNamespace = (block: string, namespaceOverrides?: Ref<string | undefined>) => {
const namespace = useGetDerivedNamespace(namespaceOverrides)
const b = (blockSuffix = '') => _bem(namespace.value, block, blockSuffix, '', '')
const e = (element?: string) => (element ? _bem(namespace.value, block, '', element, '') : '')
const m = (modifier?: string) => (modifier ? _bem(namespace.value, block, '', '', modifier) : '')
const be = (blockSuffix?: string, element?: string) =>
blockSuffix && element ? _bem(namespace.value, block, blockSuffix, element, '') : ''
const em = (element?: string, modifier?: string) =>
element && modifier ? _bem(namespace.value, block, '', element, modifier) : ''
const bm = (blockSuffix?: string, modifier?: string) =>
blockSuffix && modifier ? _bem(namespace.value, block, blockSuffix, '', modifier) : ''
const bem = (blockSuffix?: string, element?: string, modifier?: string) =>
blockSuffix && element && modifier
? _bem(namespace.value, block, blockSuffix, element, modifier)
: ''
const is: {
(name: string, state: boolean | undefined): string
(name: string): string
} = (name: string, ...args: [boolean | undefined] | []) => {
const state = args.length >= 1 ? args[0]! : true
return name && state ? `${statePrefix}${name}` : ''
}
// for css var
// --el-xxx: value;
const cssVar = (object: Record<string, string>) => {
const styles: Record<string, string> = {}
for (const key in object) {
if (object[key]) {
styles[`--${namespace.value}-${key}`] = object[key]
}
}
return styles
}
// with block
const cssVarBlock = (object: Record<string, string>) => {
const styles: Record<string, string> = {}
for (const key in object) {
if (object[key]) {
styles[`--${namespace.value}-${block}-${key}`] = object[key]
}
}
return styles
}
const cssVarName = (name: string) => `--${namespace.value}-${name}`
const cssVarBlockName = (name: string) => `--${namespace.value}-${block}-${name}`
return {
namespace,
b,
e,
m,
be,
em,
bm,
bem,
is,
// css
cssVar,
cssVarName,
cssVarBlock,
cssVarBlockName,
}
}
export type UseNamespaceReturn = ReturnType<typeof useNamespace><template>
<Transition :name="ns.b()" v-on="on">
<slot />
</Transition>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
// 从element-plus 抄来的, https://github.com/element-plus/element-plus/blob/dev/packages/components/collapse-transition/src/collapse-transition.vue
import type { RendererElement } from 'vue'
import { useNamespace } from '../hooks/useNamespace'
defineOptions({
name: 'CollapseTransition',
})
const ns = useNamespace('collapse-transition')
const reset = (el: RendererElement) => {
el.style.maxHeight = ''
el.style.overflow = el.dataset.oldOverflow
el.style.paddingTop = el.dataset.oldPaddingTop
el.style.paddingBottom = el.dataset.oldPaddingBottom
}
const on = {
beforeEnter(el: RendererElement) {
if (!el.dataset) el.dataset = {}
el.dataset.oldPaddingTop = el.style.paddingTop
el.dataset.oldPaddingBottom = el.style.paddingBottom
el.style.maxHeight = 0
el.style.paddingTop = 0
el.style.paddingBottom = 0
},
enter(el: RendererElement) {
el.dataset.oldOverflow = el.style.overflow
if (el.scrollHeight !== 0) {
el.style.maxHeight = `${el.scrollHeight}px`
} else {
el.style.maxHeight = 0
}
el.style.paddingTop = el.dataset.oldPaddingTop
el.style.paddingBottom = el.dataset.oldPaddingBottom
el.style.overflow = 'hidden'
},
afterEnter(el: RendererElement) {
el.style.maxHeight = ''
el.style.overflow = el.dataset.oldOverflow
},
enterCancelled(el: RendererElement) {
reset(el)
},
beforeLeave(el: RendererElement) {
if (!el.dataset) el.dataset = {}
el.dataset.oldPaddingTop = el.style.paddingTop
el.dataset.oldPaddingBottom = el.style.paddingBottom
el.dataset.oldOverflow = el.style.overflow
el.style.maxHeight = `${el.scrollHeight}px`
el.style.overflow = 'hidden'
},
leave(el: RendererElement) {
if (el.scrollHeight !== 0) {
el.style.maxHeight = 0
el.style.paddingTop = 0
el.style.paddingBottom = 0
}
},
afterLeave(el: RendererElement) {
reset(el)
},
leaveCancelled(el: RendererElement) {
reset(el)
},
}
</script>/*
* 提取自element-plus https://github.com/element-plus/element-plus/blob/dev/packages/theme-chalk/src/common/transition.scss
*/
:root {
--el-transition-duration: 0.3s;
--el-transition-duration-fast: 0.2s;
--el-transition-function-ease-in-out-bezier: cubic-bezier(0.645, 0.045, 0.355, 1);
--el-transition-function-fast-bezier: cubic-bezier(0.23, 1, 0.32, 1);
--el-transition-all: all var(--el-transition-duration)
var(--el-transition-function-ease-in-out-bezier);
--el-transition-fade: opacity var(--el-transition-duration)
var(--el-transition-function-fast-bezier);
--el-transition-md-fade: transform var(--el-transition-duration)
var(--el-transition-function-fast-bezier),
opacity var(--el-transition-duration) var(--el-transition-function-fast-bezier);
--el-transition-fade-linear: opacity var(--el-transition-duration-fast) linear;
--el-transition-border: border-color var(--el-transition-duration-fast)
var(--el-transition-function-ease-in-out-bezier);
--el-transition-box-shadow: box-shadow var(--el-transition-duration-fast)
var(--el-transition-function-ease-in-out-bezier);
--el-transition-color: color var(--el-transition-duration-fast)
var(--el-transition-function-ease-in-out-bezier);
}
.fade-in-linear-enter-active,
.fade-in-linear-leave-active {
transition: var(--el-transition-fade-linear);
}
.fade-in-linear-enter-from,
.fade-in-linear-leave-to {
opacity: 0;
}
.el-fade-in-linear-enter-active,
.el-fade-in-linear-leave-active {
transition: var(--el-transition-fade-linear);
}
.el-fade-in-linear-enter-from,
.el-fade-in-linear-leave-to {
opacity: 0;
}
.el-fade-in-enter-active,
.el-fade-in-leave-active {
transition: all var(--el-transition-duration) cubic-bezier(0.55, 0, 0.1, 1);
}
.el-fade-in-enter-from,
.el-fade-in-leave-active {
opacity: 0;
}
.el-fade-in-enter-active,
.el-fade-in-leave-active {
transition: all var(--el-transition-duration) cubic-bezier(0.55, 0, 0.1, 1);
}
.el-fade-in-enter-from,
.el-fade-in-leave-active {
opacity: 0;
}
.el-zoom-in-center-enter-active,
.el-zoom-in-center-leave-active {
transition: all var(--el-transition-duration) cubic-bezier(0.55, 0, 0.1, 1);
}
.el-zoom-in-center-enter-from,
.el-zoom-in-center-leave-active {
opacity: 0;
transform: scaleX(0);
}
.el-zoom-in-top-enter-active,
.el-zoom-in-top-leave-active {
opacity: 1;
transform: scaleY(1);
transition: var(--el-transition-md-fade);
transform-origin: center top;
}
.el-zoom-in-top-enter-active[data-popper-placement^='top'],
.el-zoom-in-top-leave-active[data-popper-placement^='top'] {
transform-origin: center bottom;
}
.el-zoom-in-top-enter-from,
.el-zoom-in-top-leave-active {
opacity: 0;
transform: scaleY(0);
}
.el-zoom-in-bottom-enter-active,
.el-zoom-in-bottom-leave-active {
opacity: 1;
transform: scaleY(1);
transition: var(--el-transition-md-fade);
transform-origin: center bottom;
}
.el-zoom-in-bottom-enter-from,
.el-zoom-in-bottom-leave-active {
opacity: 0;
transform: scaleY(0);
}
.el-zoom-in-left-enter-active,
.el-zoom-in-left-leave-active {
opacity: 1;
transform: scale(1, 1);
transition: var(--el-transition-md-fade);
transform-origin: top left;
}
.el-zoom-in-left-enter-from,
.el-zoom-in-left-leave-active {
opacity: 0;
transform: scale(0.45, 0.45);
}
.collapse-transition {
transition:
var(--el-transition-duration) height ease-in-out,
var(--el-transition-duration) padding-top ease-in-out,
var(--el-transition-duration) padding-bottom ease-in-out;
}
.el-collapse-transition-leave-active,
.el-collapse-transition-enter-active {
transition:
var(--el-transition-duration) max-height ease-in-out,
var(--el-transition-duration) padding-top ease-in-out,
var(--el-transition-duration) padding-bottom ease-in-out;
}
.horizontal-collapse-transition {
transition:
var(--el-transition-duration) width ease-in-out,
var(--el-transition-duration) padding-left ease-in-out,
var(--el-transition-duration) padding-right ease-in-out;
}
.el-list-enter-active,
.el-list-leave-active {
transition: all 1s;
}
.el-list-enter-from,
.el-list-leave-to {
opacity: 0;
transform: translateY(-30px);
}
.el-list-leave-active {
position: absolute !important;
}
.el-opacity-transition {
transition: opacity var(--el-transition-duration) cubic-bezier(0.55, 0, 0.1, 1);
}@import './transition.css';
// ...容器组件本体
新建packages/container/components/DemoPreview.vue
简单说明一下
- 默认插槽是用来装载使用虚拟模块包装处理后的示例代码
highlight具名插槽是用来装载经过markdown-it高亮处理后的源码
查看
<template>
<ClientOnly>
<section :class="[$style.example]">
<div :class="$style['example-showcase']">
<slot />
</div>
<div :class="$style['example-divider--horizontal']"></div>
<div :class="$style['example-actions']">
<Tooltip placement="top" :content="locale['edit-in-playground']">
<Playground v-if="lang === 'vue'" style="cursor: pointer" :code="decodedSource" />
</Tooltip>
<div :class="$style['example-actions--right']">
<Tooltip placement="top" :content="locale['copy-code']">
<Copy style="cursor: pointer" @click="copyCode" />
</Tooltip>
<Tooltip placement="top" :content="locale['view-source']">
<Code style="cursor: pointer" @click="toggleExpanded" />
</Tooltip>
</div>
<span v-show="copyTip" :class="$style['example-actions-tip']">{{
locale['copy-success']
}}</span>
</div>
<CollapseTransition>
<div v-show="isExpanded" :class="$style['example-source-wrapper']">
<template v-if="isFile">
<div :class="`example-source language-${lang}`">
<span class="lang">{{ lang }}</span>
<div v-html="decodedHlSource"></div>
</div>
</template>
<slot v-else name="highlight" />
</div>
</CollapseTransition>
<Transition name="el-fade-in-linear">
<div v-show="isExpanded" :class="$style['example-control']" @click="toggleExpanded">
<span :class="$style['control-icon']"></span>
<span :class="$style['control-text']">{{ locale['hide-source'] }}</span>
</div>
</Transition>
</section>
</ClientOnly>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref, defineProps, computed } from 'vue'
import CollapseTransition from './CollapseTransition.vue'
import Tooltip from './Tooltip.vue'
import Playground from './icons/SfcPlayground.vue'
import Copy from './icons/Copy.vue'
import Code from './icons/Code.vue'
import { useCopyCode } from '../hooks/useCopyCode'
import '../style/index.css'
interface DemoProps {
lang: string // 源码类型
source: string // 转码后的源码内容
isFile: boolean // 是否为引入文件的模式
hlSource?: string // 转码后的markdown高亮源码
}
defineOptions({
name: 'DemoPreview',
})
const props = withDefaults(defineProps<DemoProps>(), {
lang: 'vue',
isFile: false,
hlSource: '',
})
const locale = computed(() => {
return {
'view-source': '查看源代码',
'hide-source': '隐藏源代码',
'edit-in-playground': '在 Playground 中编辑',
'copy-code': '复制代码',
'copy-success': '复制成功',
}
})
const decodedSource = computed(() => decodeURIComponent(props.source))
const decodedHlSource = computed(() => decodeURIComponent(props.hlSource))
const isExpanded = ref(false)
const toggleExpanded = () => {
isExpanded.value = !isExpanded.value
}
const { copyTip, copyCode } = useCopyCode(decodedSource.value)
</script>
<style module>
:global(.vp-doc .example-source[class*='language-']) {
margin: 0;
border-radius: 0;
}
:global(.example-source[class*='language-'] code) {
padding: 0 1rem;
}
.example {
border: 1px solid var(--preview-border);
border-radius: 1px;
margin: 20px 0 50px;
}
.example-showcase {
padding: 1rem;
color: var(--preview-text-1);
background-color: var(--preview-bg);
}
.example-divider--horizontal {
display: block;
height: 1px;
width: 100%;
}
.example-actions {
position: relative;
display: flex;
height: 40px;
padding: 0 8px;
align-items: center;
justify-content: space-between;
border-top: 1px dashed var(--preview-divider);
}
.example-actions--right {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
gap: 15px;
}
.example-source-wrapper {
overflow: hidden;
border-top: 1px dashed var(--preview-divider);
transition: 0.3s;
}
.example-control {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
border-top: 1px solid var(--preview-border);
height: 44px;
box-sizing: border-box;
background-color: var(--preview-bg);
color: var(--preview-text-2);
cursor: pointer;
position: sticky;
left: 0;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
z-index: 10;
}
.example-control .control-text {
margin-left: 10px;
font-size: 14px;
}
.control-icon {
content: '';
width: 0;
height: 0;
border-right: 6px solid transparent;
border-left: 6px solid transparent;
border-bottom: 6px solid var(--preview-text-3);
}
.example-control:hover .control-icon {
border-bottom-color: var(--preview-primary-color);
}
.example-control:hover {
color: var(--preview-primary-color);
}
.example-actions-tip {
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%);
font-size: 14px;
color: var(--preview-green-3);
}
</style>图标组件
其中SfcPlayground.vue图标是用来把源码发送到 Vue 官方的演练场进行演示的
<template>
<svg
t="1596458647160"
class="icon"
viewBox="0 0 1024 1024"
version="1.1"
xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"
p-id="2840"
xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink"
width="18"
height="18"
>
<path
d="M311.1 739c-6.1 0-12.2-2.3-16.8-7L69.7 507.4l224.6-224.6c9.3-9.3 24.3-9.3 33.6 0s9.3 24.3 0 33.6l-191 191 191 191c9.3 9.3 9.3 24.3 0 33.6-4.6 4.7-10.7 7-16.8 7zM711.5 739c-6.1 0-12.2-2.3-16.8-7-9.3-9.3-9.3-24.3 0-33.6l191-191-191-191c-9.3-9.3-9.3-24.3 0-33.6s24.3-9.3 33.6 0L953 507.4 728.3 732c-4.6 4.7-10.7 7-16.8 7zM418.5 814.7c-2.4 0-4.8-0.4-7.2-1.1-12.5-4-19.4-17.3-15.5-29.8l179.6-567.1c4-12.5 17.3-19.4 29.8-15.5 12.5 4 19.4 17.3 15.5 29.8L441.1 798.1a23.73 23.73 0 0 1-22.6 16.6z"
fill="#666"
p-id="2841"
></path>
</svg>
</template><template>
<svg
t="1596458734865"
class="icon"
viewBox="0 0 1024 1024"
version="1.1"
xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"
p-id="4898"
xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink"
width="14"
height="14"
>
<path
d="M68.608 962.56V206.848h740.864V962.56H68.608zM746.496 271.36H131.584v629.248h614.912V271.36zM131.584 262.144"
p-id="4899"
fill="#666"
></path>
<path
d="M219.136 65.024v116.224h62.976V129.536h614.912v629.248h-60.416v61.952h123.392V65.024z"
p-id="4900"
fill="#666"
></path>
</svg>
</template><script lang="ts" setup>
import { computed } from 'vue'
const props = defineProps<{ code: string }>()
const sfcBaseUrl = 'https://play.vuejs.org/'
const sfcPlaygroundUrl = computed(() => {
const sfcJson = { 'App.vue': props.code }
return `${sfcBaseUrl}#${btoa(unescape(encodeURIComponent(JSON.stringify(sfcJson))))}`
})
</script>
<template>
<a :href="sfcPlaygroundUrl" target="_blank">
<svg
version="1.1"
id="Layer_1"
xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"
xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink"
widht="16"
height="16"
viewBox="0 0 1024 1024"
xml:space="preserve"
>
<g>
<path
d="M1004.57 319.408l-468-312c-15.974-9.83-33.022-9.92-49.142 0l-468 312C7.428 327.406 0 341.694 0 355.978v311.998c0 14.286 7.428 28.572 19.43 36.572l468 312.044c15.974 9.83 33.022 9.92 49.142 0l468-312.044c12-7.998 19.43-22.286 19.43-36.572V355.978c-0.002-14.284-7.43-28.572-19.432-36.57zM556 126.262l344.572 229.716-153.714 102.858L556 331.406V126.262z m-88 0v205.144l-190.858 127.43-153.714-102.858L468 126.262zM88 438.264l110.286 73.714L88 585.692v-147.428z m380 459.43L123.428 667.978l153.714-102.858L468 692.55v205.144z m44-281.716l-155.43-104 155.43-104 155.43 104-155.43 104z m44 281.716V692.55l190.858-127.43 153.714 102.858L556 897.694z m380-312.002l-110.286-73.714L936 438.264v147.428z"
p-id="2793"
fill="#555"
/>
</g>
</svg>
</a>
</template>导出container项目
新建packages/container/index.ts
export * from './hooks'
export { default } from './components/DemoPreview.vue'plugin项目开发
安装相关依赖
pnpm add markdown-it markdown-it-container hash-sum --filter ./packages/plugin
pnpm add unified remark-parse remark-stringify remark-frontmatter --filter ./packages/plugin
pnpm add -D @types/markdown-it @types/markdown-it-container @types/hash-sum --filter ./packages/plugin
pnpm add -D vite @types/unist --filter ./packages/pluginmarkdown插件
我们先只考虑在 markdown 的自定义容器中内嵌代码块的情况
新建packages/plugin/index.ts,然后编辑docs/.vitepress/config.ts把这个demoPreviewPlugin函数在 VitePress 的配置中注册一下
代码先暂时这样写,后续会补全逻辑,我们先来看看markdown-it中的tokens流是个什么东西
查看
import type MarkdownIt from 'markdown-it'
import container from 'markdown-it-container'
/**
* markdown 插件的配置参数
*/
interface PreviewPluginOptions {
/** docs文档路径 */
docRoot: string
/** 自定义容器组件名 */
componentName?: string
}
/**
* markdown插件,用来解析demo代码
* @param md
* @param options
*/
export function demoPreviewPlugin(md: MarkdownIt, options: PreviewPluginOptions = { docRoot: '' }) {
options.componentName = options.componentName || 'DemoPreview'
md.use(createDemoContainer, options)
}
/**
* 自定义容器,也就是用:::demo ::: 包裹起来的部分
* @param md
* @param options
*/
function createDemoContainer(md: MarkdownIt, options: PreviewPluginOptions) {
const { componentName = 'DemoPreview', docRoot } = options
md.use(container, 'demo', {
validate(params: string) {
return !!params.trim().match(/^demo\s*(.*)$/)
},
render(tokens: MarkdownIt.Token[], idx: number) {
console.log('createDemoContainer =>', tokens)
const token = tokens[idx]
// 开始标签的 nesting 为 1,结束标签的 nesting 为 -1
if (token.nesting === 1 && token.type === 'container_demo_open') {
const lang = tokens[idx + 1].info
const source = tokens[idx + 1].type === 'fence' ? tokens[idx + 1].content : ''
// 这个componentName表示之后注册组件时所使用的组件名
return `<${componentName} lang="${lang}" source="${encodeURIComponent(source)}">`
}
// 结束标签
return `</${componentName}>`
},
})
}import { fileURLToPath, URL } from 'node:url'
import { demoPreviewPlugin } from '../../packages/plugin'
export default defineConfig({
// ...
markdown: {
config: (md) => {
const docRoot = fileURLToPath(new URL('../', import.meta.url))
md.use(demoPreviewPlugin, { docRoot })
},
},
})编辑docs示例项目的markdown-examples.md文件,把原本的内容清空掉,填入以下内容,然后启动示例项目
:::demo
```vue
<template>
<div>{{ title }}</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, defineComponent } from 'vue'
const title = ref('this is basic demo')
</script>
```
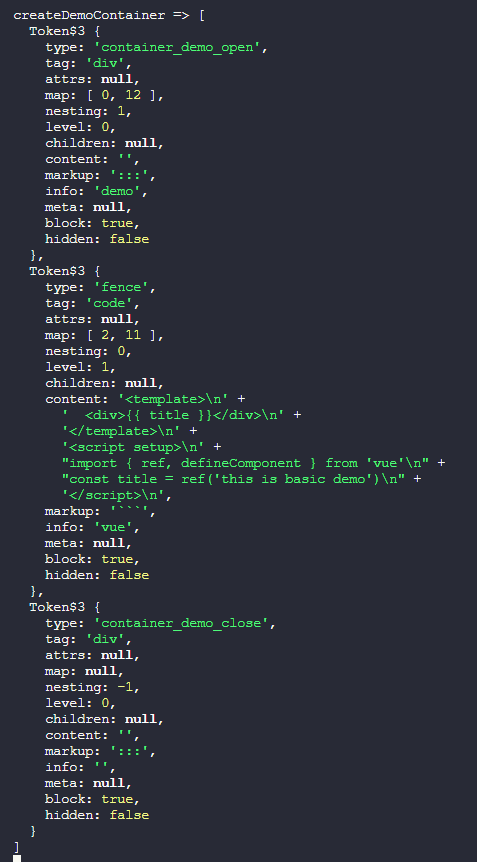
:::可以看到终端输出了以下内容
通过观察发现,tokens流是个对象数组,对象中的type值为container_demo_open且nesting为1时代表我们的自定义容器的开始标签;type值为fence的时候就是容器内部的代码块
新建docs/examples/Input.vue,在里面随便写点vue的代码
再编辑一下markdown-examples.md文件,添加如下内容,这表示在自定义容器中引入文件
:::demo src=examples/Input.vue
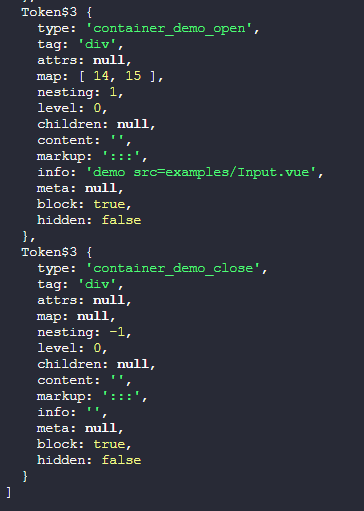
:::观察一下终端的输出可以看到,这次输出的tokens中没有type值为fence的节点数据了
了解以上这些规律后,我们就可以来补全markdown插件的代码了
编辑packages/plugin/index.ts
查看
import fs from 'node:fs'
import path from 'node:path'
import type MarkdownIt from 'markdown-it'
import container from 'markdown-it-container'
/**
* markdown插件,用来解析demo代码
* @param md
* @param options
*/
export function demoPreviewPlugin(md: MarkdownIt, options: PreviewPluginOptions = { docRoot: '' }) {
options.componentName = options.componentName || 'DemoPreview'
md.use(createDemoContainer, options)
md.use(renderDemoCode)
}
/**
* 自定义容器,也就是用:::demo ::: 包裹起来的部分
* @param md
* @param options
*/
function createDemoContainer(md: MarkdownIt, options: PreviewPluginOptions) {
const { componentName = 'DemoPreview', docRoot } = options
md.use(container, 'demo', {
validate(params: string) {
return !!params.trim().match(/^demo\s*(.*)$/)
},
render(tokens: MarkdownIt.Token[], idx: number) {
const token = tokens[idx]
// 开始标签的 nesting 为 1,结束标签的 nesting 为 -1
if (token.nesting === 1 && token.type === 'container_demo_open') {
const m = token.info.trim().match(/^demo\s*(src=.*)?$/)
const sourceFile = m && m.length > 1 ? m[1]?.split('=')[1].trim() : ''
let source = ''
let lang = ''
if (sourceFile) {
lang = path.extname(sourceFile).slice(1)
source = fs.readFileSync(path.resolve(docRoot, sourceFile), 'utf-8')
if (!source) throw new Error(`Incorrect source file: ${sourceFile}`)
} else {
lang = tokens[idx + 1].info
source = tokens[idx + 1].type === 'fence' ? tokens[idx + 1].content : ''
}
// 这个componentName表示之后注册组件时所使用的组件名
return `<${componentName} :isFile="${!!sourceFile}" hlSource="${encodeURIComponent(
md.options.highlight?.(source, lang, '') ?? ''
)}" lang="${lang}" source="${encodeURIComponent(source)}">`
}
// 结束标签
return `</${componentName}>`
},
})
}
/**
* 解析渲染自定义容器内部的代码块
* @param md
*/
function renderDemoCode(md: MarkdownIt) {
// 这个 fence 就类似 ```vue ... ``` 代码块中的那个vue标识
const defaultRender = md.renderer.rules.fence!
md.renderer.rules.fence = (...args) => {
const [tokens, idx] = args
const token = tokens[idx]
// 判断该 fence 是否在 ::: demo 内
const prevToken = tokens[idx - 1]
const isInDemoContainer =
prevToken && prevToken.nesting === 1 && prevToken.info.trim().match(/^demo\s*(.*)$/)
const lang = token.info.trim()
// 如果在demo内的话就进行自定义渲染
if (isInDemoContainer) {
return `
<template #highlight>
<div v-pre class="example-source language-${lang}" >
<span class="lang">${lang}</span>
${md.options.highlight?.(token.content, lang, '')}
</div>
</template>`
}
return defaultRender?.(...args)
}
}Vite插件
首先编写的是configResolved和transform这两个钩子函数。configResolved用来收集需要用到的 Vite 配置,而transform则是用来解析 markdown 文件,提取出自定义 markdown 容器中的代码块,并将其转换为虚拟 Vue 组件模块。
编辑packages/plugin/index.ts,增加如下viteDemoPreviewPlugin函数
接着再编辑docs/vite.config.ts把这个viteDemoPreviewPlugin函数在 Vite 配置中注册一下
代码先暂时这样写,我们来看看transform钩子的两个参数具体是个什么东西
import type { Plugin } from 'vite'
/**
* vite插件, 用来转换markdown中的demo代码
*/
export function viteDemoPreviewPlugin(): Plugin {
// 用来收集已挂载的vite插件,因为在HMR那里需要手动更新
let vitePlugin: any
const options = {
mode: 'vitepress',
root: '',
}
return {
name: 'vite-plugin-code-preview',
enforce: 'pre',
async configResolved(config) {
const isVitepress = config.plugins.find((p) => p.name === 'vitepress')
vitePlugin = config.plugins.find((p) => p.name === 'vite:vue')
options.mode = isVitepress ? 'vitepress' : 'vite'
options.root = path.resolve(config.root) // 提前抹平系统差异
},
// 把markdown中的demo代码块转换成组件
async transform(code, id) {
if (!id.endsWith('.md')) return
console.log('transform.id =>', id)
console.log('transform.code =>', code)
return code
},
}
}import { viteDemoPreviewPlugin } from '../packages/plugin'
export default defineConfig({
plugins: [vueJsx(), viteDemoPreviewPlugin()],
})编辑一下markdown-examples.md文件,再次添加如下内容
<script setup>
console.log('setup in markdown')
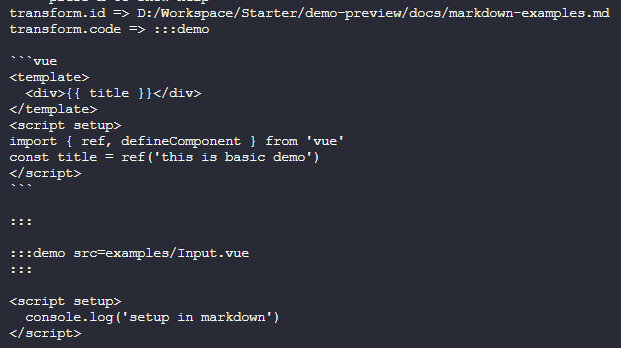
</script>启动docs示例项目,可以看到终端输出了以下内容
其中id就是 markdown 文件的路径,code就是 markdown 文件的内容
知道了这些信息后,我们就可以开始着手编写解析 markdown 文件内容的逻辑了
解析markdown
新建packages/plugin/remark.ts编写如下的markdownToComponent函数,接着编辑packages/plugin/index.ts,在transform钩子中调用markdownToComponent函数
代码先暂时这样,我们先来看看remark会把 markdown 文件内容解析成什么样
import { unified } from 'unified'
import remarkParse from 'remark-parse'
import remarkFrontmatter from 'remark-frontmatter'
import remarkStringify from 'remark-stringify'
/**
* 把markdown中的demo代码转换为组件
* @param code markdown的原始内容
* @param id 模块id
* @param root docs文档根目录
*/
export async function markdownToComponent(code: string, id: string, root: string) {
// 解析markdown文件
const parsed = await unified()
.use(remarkParse) // 实例化parser, 用于生成 mdast
.use(remarkFrontmatter) // 处理markdown的元信息
.use(remarkStringify) // 实例化compiler, 用于将经过人为处理后的 mdast 输出为 markdown
.process(code) // 执行解析
console.log('markdownToComponent =>', parsed)
}import { markdownToComponent } from './remark'
export function viteDemoPreviewPlugin(): Plugin {
// ...
return {
// ...
async transform(code, id) {
if (!id.endsWith('.md')) return
await markdownToComponent(code, path.resolve(id), options.root)
return code
},
}
}可以看到,remark解析后的结果是一个虚拟文件对象,它是从mdast抽象语法树转换得来,里面包含了 markdown 文件中的所有内容,包括元信息、代码块
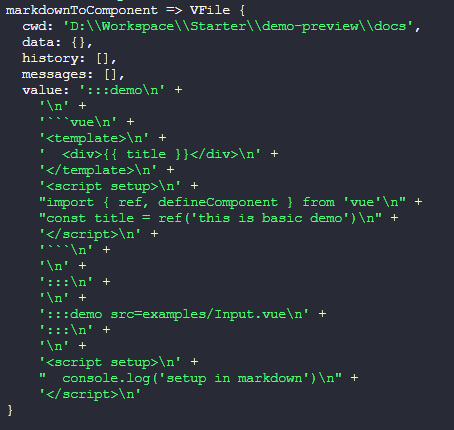
那么,如何从mdast抽象语法树中获取成我们想要的代码并转换成组件呢?答案就是remark的插件机制
我们可以自定义一个插件方法供remark的use管道进行调用,然后在这自定义的插件方法中提取出我们想要的 markdown 内容,然后转换成 Vue 组件
好,我们这就来试一试,把markdownToComponent函数改造一下,看看这次在终端中输出什么
import type { Node } from 'unist'
interface ExtraNode extends Node {
children?: Array<ExtraNode>
[key: string]: any
}
export async function markdownToComponent(code: string, id: string, root: string) {
// 解析markdown文件
const parsed = await unified()
.use(remarkParse) // 实例化parser, 用于生成 mdast
.use(remarkFrontmatter) // 处理markdown的元信息
.use(() => (tree: ExtraNode) => {
console.log('markdownToComponent =>', tree)
})
.use(remarkStringify) // 实例化compiler, 用于将经过人为处理后的 mdast 输出为 markdown
.process(code) // 执行解析
}可以看到,这次输出的是mdast抽象语法树结构的数据了
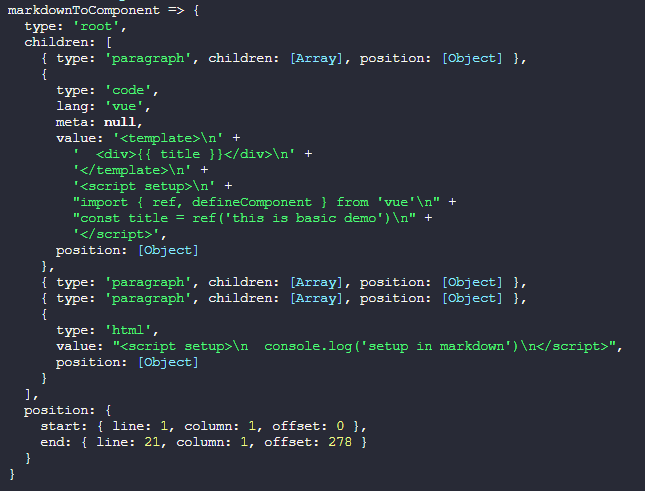
我们再改造一下自定义的remark插件方法,对mdast抽象语法树进行遍历一下
const parsed = await unified()
.use(remarkParse) // 实例化parser, 用于生成 mdast
.use(remarkFrontmatter) // 处理markdown的元信息
.use(() => (tree: ExtraNode) => {
tree.children?.forEach((node, index) => {
console.log('markdownToComponent =>', node)
})
})
.use(remarkStringify) // 实例化compiler, 用于将经过人为处理后的 mdast 输出为 markdown
.process(code) // 执行解析可以看到,这次输出的内容就完整了,观察一下找出规律,大致可以得出
- 每个节点如果存在
children字段并且其下标0的元素中的value字段以:::demo开头的话就是我们的自定义容器的起始标签 - 起始标签的下一个节点就是代码块的内容,其中
lang表示代码块的语言类型,value就是代码内容 - 如果是引入文件的情况,
:::demo后面会带有src=xxx之类的内容,可以使用正则表达式提取出来 - 如果 markdown 中直接插入 html 标签的话,节点数据中的
type值为html,而value就是这个标签对的内容(含标签)
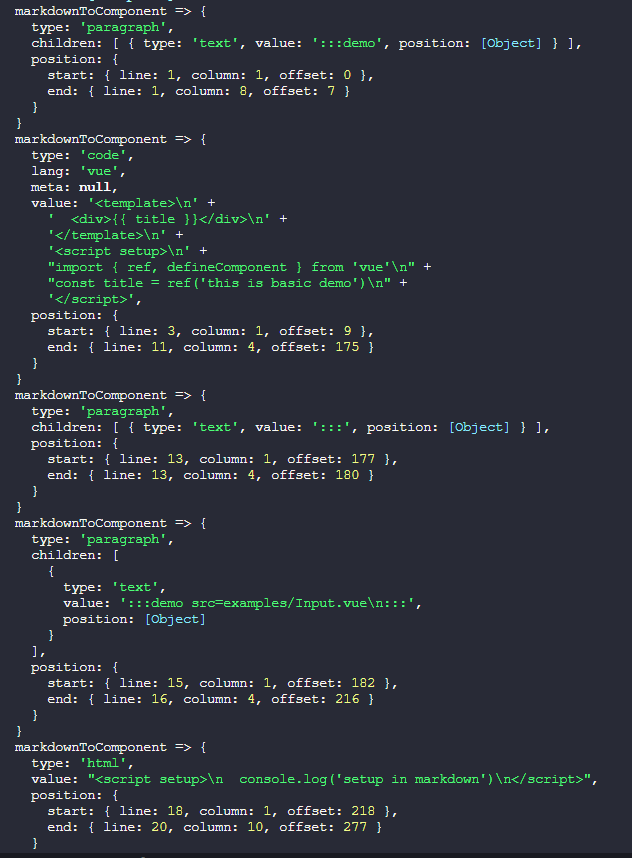
得到以上规律后,我们来补全一下markdownToComponent函数的逻辑
查看
import os from 'os'
import fs from 'fs'
import path from 'path'
import { unified } from 'unified'
import remarkParse from 'remark-parse'
import remarkFrontmatter from 'remark-frontmatter'
import remarkStringify from 'remark-stringify'
import type { Node } from 'unist'
import hash from 'hash-sum'
interface ExtraNode extends Node {
children?: Array<ExtraNode>
[key: string]: any
}
// 因为一个markdown文件就相当于一个SFC组件,所以只能存在一个setup,这个正则就是用来尝试找出是否已有setup
const ScriptSetupRegex = /^<script\s(.*\s)?setup(\s.*)?>([\s\S]*)<\/script>$/
/**
* 将markdown文件和哈希值组合成虚拟模块名
* @param id 模块id
* @param key 代码块哈希值
* @param lang 代码块所属语言
*/
const combineVirtualModule = (id: string, key: string, lang: string) =>
`virtual:${path.basename(id)}.${key}.${lang}`
/**
* 把markdown中的demo代码转换为组件
* @param code markdown的原始内容
* @param id 模块id
* @param root docs文档根目录
*/
export async function markdownToComponent(code: string, id: string, root: string) {
// 用来收集markdown中的demo代码块
const _blocks: { lang: string; code: string; key: string }[] = []
// 解析markdown文件
const parsed = await unified()
.use(remarkParse) // 实例化parser, 用于生成 mdast
.use(remarkFrontmatter) // 处理markdown的元信息
.use(() => (tree: ExtraNode) => {
let seed = 0
const scriptSetup = { index: -1, content: '' }
tree.children?.forEach((node, index) => {
try {
// 判断是否已经存在 script setup 标签, 注释的忽略不处理
if (node.type === 'html') {
const m = node.value.trim().match(ScriptSetupRegex)
if (!m) return false
scriptSetup.index = index
scriptSetup.content = m[3] ?? ''
}
if (!node.children || !node.children[0].value) return false
// 判断demo容器是否为内联代码块的模式
const hasDemo = node.children[0].value.trim().match(/demo\s*(.*)$/)
const nextNodeIsCode = hasDemo && tree.children![index + 1].type === 'code'
// 下一个节点如果是内联代码块的话
if (nextNodeIsCode) {
const hashKey = hash(`${id}-demo-${seed}`)
_blocks.push({
lang: tree.children![index + 1].lang,
code: tree.children![index + 1].value,
key: hashKey, // 每个代码块的唯一key
})
node.children[0].value += ` Virtual-${hashKey}`
seed++
}
// 判断demo容器是否为引入文件的模式
const hasSrc = node.children[0].value.trim().match(/^:::demo\s*(src=.*)\s*:::$/)
if (hasSrc) {
const markdownId = path.relative(root, id)
const sourceFile = hasSrc && hasSrc.length > 1 ? hasSrc[1]?.split('=')[1].trim() : ''
// 记录当前markdown使用了哪些组件
handleCacheFile(markdownId, path.join(sourceFile))
const lang = path.extname(sourceFile).slice(1)
const source = fs.readFileSync(path.resolve(root, sourceFile), 'utf-8')
const hashKey = hash(`${id}-demo-${seed}`)
_blocks.push({
lang,
code: source,
key: hashKey,
})
node.children[0].value = `:::demo src=${sourceFile} Virtual-${hashKey}${os.EOL}:::`
seed++
}
} catch (error) {
console.error('parse markdown error in function transformCodeToComponent')
return false
}
})
if (_blocks.length === 0) return
const virtualModules = _blocks
.map((b) => {
const moduleName = combineVirtualModule(id, b.key, b.lang)
return `import Virtual${b.key} from '${moduleName}'`
})
.join(os.EOL)
// 如果之前已经有一个 setup 的话,那就把虚拟模块塞进去
if (scriptSetup.index !== -1) {
const node = tree.children![scriptSetup.index]
node.value = node.value.replace(ScriptSetupRegex, (m: string, ...args: string[]) => {
return `<script ${args[0] ?? ''} setup ${args[1] ?? ''}>${os.EOL}${virtualModules}${
os.EOL
}${args[2] ?? ''}</script>`
})
} else {
// 如果没有setup的话,就新增一个用来将虚拟模块追加到markdown
tree.children?.push({
type: 'html',
value: `<script setup>${os.EOL}${virtualModules}${os.EOL}</script>`,
})
}
})
.use(remarkStringify) // 实例化compiler, 用于将经过人为处理后的 mdast 输出为 markdown
.process(code) // 执行解析
const blocks = _blocks.map((b) => {
const moduleName = combineVirtualModule(id, b.key, b.lang)
cacheCode.set(b.key, b.code)
return { ...b, id: moduleName }
})
return { parsedCode: String(parsed), blocks }
}
/**
* 将markdown文件和所引用的组件关系缓存起来
* @param mdId markdown 文件
* @param file 组件
*/
function handleCacheFile(mdId: string, file: string) {
const prev: string[] = cacheFile.get(mdId) ?? []
const files = Array.from(new Set([...prev.filter(Boolean), file]))
cacheFile.set(mdId, files)
}
export const cacheCode = new Map<string, string>()
export const cacheFile = new Map<string, string[]>()⚡ 简单解释一下
ScriptSetupRegex这个正则表达式是用来匹配 markdown 文件中是否已经存在一个带setup的<script>标签;如果存在,就把虚拟模块塞进这个标签中,否则就创建一个<script setup>标签。之所以这么做是因为 Vue 规定了每个 SFC 组件只能存在一个<script setup>标签,而 VitePress 会把 markdown 文件解析成一个 SFC 组件_blocks数组是用来收集自定义 markdown 容器中的代码块内容,在remark解析完毕后对收集到的代码块进行遍历,并使用cacheCode这个Map对象将其缓存下来,同时将其转为虚拟模块hash-sum这个包的作用是根据指定的参数生成哈希值,以保证每次遍历 markdown 文件时的哈希值不会改变Virtual-${hashKey}追加到:::demo的后面是为了给 markdown 渲染时用的,它在渲染成VNode时表示虚拟组件的插入点- 当使用引入文件的模式时,
cacheFile这个Map对象是用来保存每个 markdown 文件所引用到的文件,手动管理 HMR 更新时需要用到
resolveId和load钩子
markdownToComponent函数的逻辑完成后,我们修改一下transform钩子,拿到它的返回值
export function viteDemoPreviewPlugin(): Plugin {
// ...
return {
// ...
async transform(code, id) {
if (!id.endsWith('.md')) return
const { parsedCode } = await markdownToComponent(code, path.resolve(id), options.root)
return { code: parsedCode, map: null }
},
}
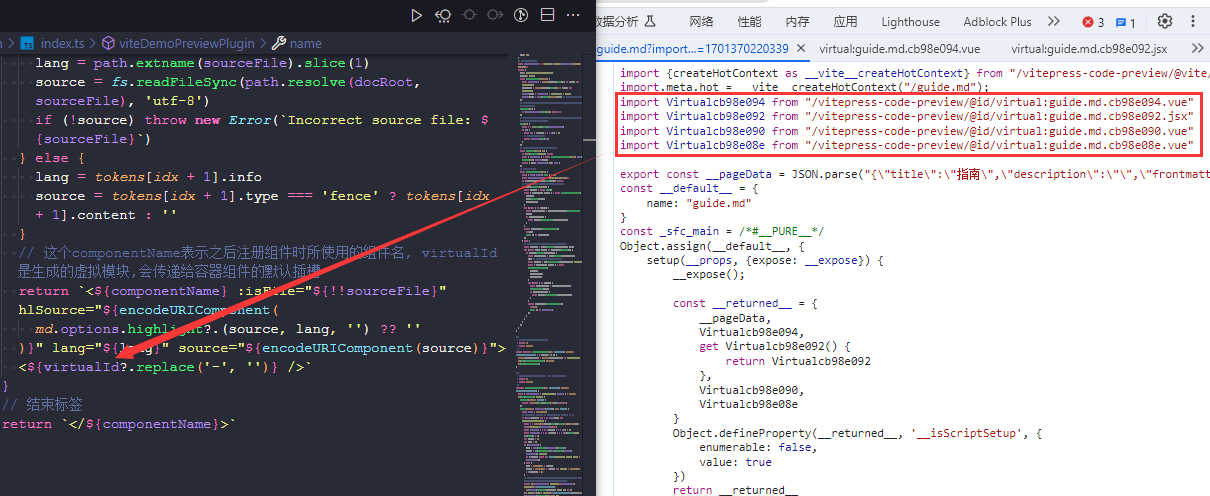
}这时,示例项目应该会出现类似下面这样的错误
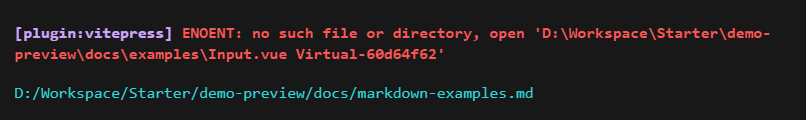
不要慌,这是因为之前的 markdown 插件中的createDemoContainer函数中的正则表达式还没有处理Virtual-${hashKey}的情况,也就是上文提到的 markdown 渲染成VNode时虚拟组件的插入点
现在来补一下
function createDemoContainer(md: MarkdownIt, options: PreviewPluginOptions) {
md.use(container, 'demo', {
// ...
render(tokens: MarkdownIt.Token[], idx: number) {
const token = tokens[idx]
if (token.nesting === 1 && token.type === 'container_demo_open') {
const m = tokens[idx].info.trim().match(/^demo\s*(src=.*\s)?(Virtual-([a-zA-Z0-9]+))?$/)
const virtualId = m && m.length > 2 ? m[2] : ''
// ...
return `<${componentName} :isFile="${!!sourceFile}" hlSource="${encodeURIComponent(
md.options.highlight?.(source, lang, '') ?? ''
)}" lang="${lang}" source="${encodeURIComponent(source)}">
<${virtualId?.replace('-', '')} />`
}
// 结束标签
return `</${componentName}>`
},
})
}上面的操作完成后重新启动docs示例项目,这时又出现新的报错,它的意思是虚拟模块的路径在文件系统中找不到,所以报错
这是因为 Vite 插件viteDemoPreviewPlugin中缺少了resolveId和load钩子函数,其中resolveId用来识别指定的虚拟模块,load用来加载被识别到的指定虚拟模块
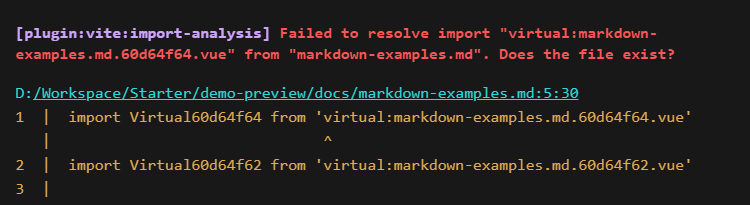
编辑viteDemoPreviewPlugin函数,补上这两个钩子
import { cacheCode, markdownToComponent } from './remark'
export function viteDemoPreviewPlugin(): Plugin {
// ...
// 用来匹配虚拟模块
const virtualModRegex = /^virtual:.*\.md\.([a-zA-Z0-9]+)\.(vue|jsx|tsx)$/
return {
// ...
// 解析虚拟模块ID,如果请求的模块ID与预期的虚拟模块ID匹配,则返回该ID,否则返回undefined
resolveId(id) {
if (virtualModRegex.test(id)) return id
},
// 加载虚拟模块的内容,如果请求的模块ID与预期的虚拟模块ID匹配,则生成模块内容并返回,否则返回undefined
load(id) {
const m = id.trim().match(virtualModRegex)
if (m) {
const key = m.length > 1 ? m[1] : ''
// 返回虚拟模块的源码
return cacheCode.get(key)
}
},
}
}这回好了,没有报错,但是页面没有显示demo内嵌代码模式的示例,咋回事?
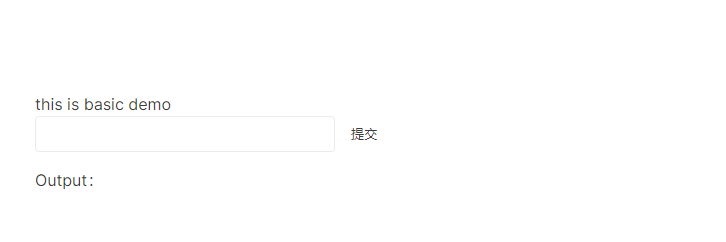
因为我们还没在 VitePress 中注册之前编写好的container容器组件
新建docs/.vitepress/theme/index.ts,添加如下代码
import type { Theme } from 'vitepress'
import DefaultTheme from 'vitepress/theme'
import DemoPreview, { useComponents } from '../../../packages/container'
export default {
...DefaultTheme,
enhanceApp(ctx) {
const { app } = ctx
useComponents(app, DemoPreview)
},
} satisfies Theme刷新页面,这回可以看到示例项目已经正确的渲染出来了
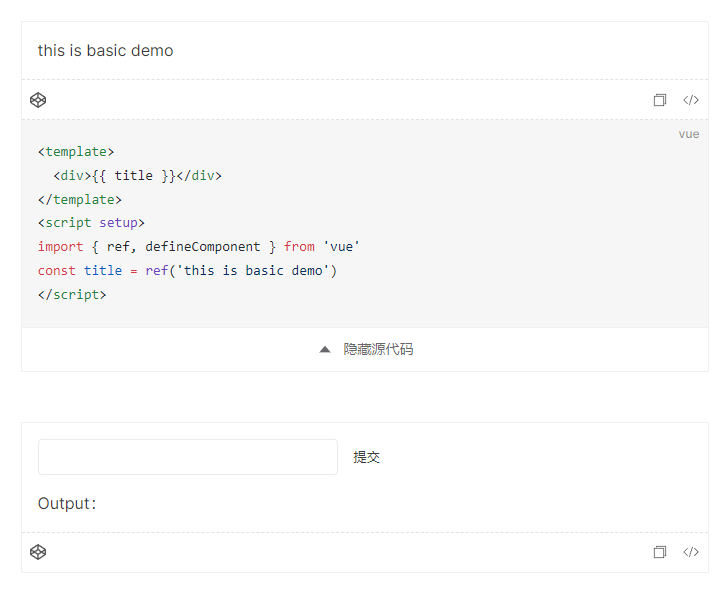
但是此时修改示例代码还不会触发重新渲染,而修改 markdown 文件虽然会触发 Vite 默认的 HMR,但不会重新加载虚拟模块。这是因为之前加载虚拟模块的代码是发生在load钩子中的,而此钩子在编译阶段成功加载到数据后就不会重复加载了,所以此时虚拟模块的代码还是旧的
handleHotUpdate钩子
修改viteDemoPreviewPlugin函数,给它增加handleHotUpdate钩子,自己维护指定虚拟模块的 HMR 行为
查看
import { cacheCode, cacheFile, markdownToComponent } from './remark'
export function viteDemoPreviewPlugin(): Plugin {
// ...
return {
// ...
// 自定义HMR更新
async handleHotUpdate(ctx) {
const { file, server, read } = ctx
const manualUpdateRegex = /\.(md|vue|jsx|tsx)$/
if (!manualUpdateRegex.test(file)) return
// 正向更新,通过markdown文件更新内部代码块
if (file.endsWith('.md')) {
const content = await read()
const { parsedCode, blocks } = await markdownToComponent(
content,
path.resolve(file),
options.root
)
for (const b of blocks) {
const virtualModule = server.moduleGraph.getModuleById(b.id)
if (virtualModule) {
await server.reloadModule(virtualModule)
}
}
return vitePlugin.handleHotUpdate({
...ctx,
read: () => parsedCode,
})
} else {
// 反向更新,通过被引用的组件来更新markdown
const fileName = path.relative(options.root, file)
for (const [key, value] of cacheFile.entries()) {
if (value.includes(fileName)) {
const markdownPath = path.resolve(options.root, key) // 组合完整的markdown文件路径
const content = fs.readFileSync(markdownPath, 'utf-8')
const { parsedCode, blocks } = await markdownToComponent(
content,
markdownPath,
options.root
)
for (const b of blocks) {
const virtualModule = server.moduleGraph.getModuleById(b.id)
if (virtualModule) {
await server.reloadModule(virtualModule)
}
}
return vitePlugin.handleHotUpdate({
...ctx,
read: () => parsedCode,
})
}
}
}
},
}
}现在,我们修改 markdown 中的示例代码,可以发现已经会触发重新渲染了
⚡ 到这里,子项目的开发工作已经完成,接下来进入打包配置环节
container项目打包
先安装一个依赖,用来给组件生成d.ts文件
pnpm add vite-plugin-dts -D --filter ./packages/container接着新建packages/container/vite.config.ts,填入如下配置
import { resolve } from 'path'
import { defineConfig } from 'vite'
import vue from '@vitejs/plugin-vue'
import dts from 'vite-plugin-dts'
export default defineConfig({
build: {
minify: false,
lib: {
entry: resolve(__dirname, './index.ts'),
name: 'preview-container',
fileName: 'index',
},
rollupOptions: {
external: ['vue', 'vite', 'vitepress'],
output: {
globals: {
vue: 'Vue',
},
},
},
},
plugins: [vue(), dts({ insertTypesEntry: true })],
})然后编辑packages/container/package.json,添加打包脚本、文件导出配置以及作者信息之类的,比如
{
"name": "@vitepress-code-preview/container",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "preview component of code and component in vitepress",
"keywords": ["Vite", "VitePress", "Vue", "plugin", "demo", "preview", "JSX", "TSX"],
"author": "welives",
"license": "MIT",
"type": "module",
"main": "./dist/index.umd.cjs",
"module": "./dist/index.js",
"types": "./dist/index.d.ts",
"exports": {
".": {
"import": "./dist/index.js",
"require": "./dist/index.umd.cjs"
},
"./dist/style.css": "./dist/style.css"
},
// 这个 files 是告诉 npm 要上传的文件有哪些
"files": ["dist", "README.md", "CHANGELOG.md", "package.json", "LICENSE"],
"scripts": {
"dev": "vite build --watch",
"build": "vite build"
},
"homepage": "https://github.com/welives/vitepress-code-preview",
"repository": {
"type": "git",
"url": "git@github.com:welives/vitepress-code-preview.git"
}
// ...
}执行container项目的打包脚本pnpm build,不出意外的话应该是打包成功的
plugin项目打包
我们使用 Rollup 来打包这个 plugin 项目,安装一下依赖
pnpm add rollup rollup-plugin-ts -D --filter ./packages/plugin新建packages/plugin/rollup.config.mjs,填入如下配置
import ts from 'rollup-plugin-ts'
export default {
input: 'index.ts',
output: [
{
file: 'dist/index.cjs',
format: 'cjs',
},
{
file: 'dist/index.js',
format: 'es',
},
],
plugins: [ts()],
watch: { exclude: 'node_modules/**' },
external: ['vite', 'vitepress'],
}编辑packages/plugin/package.json,和container项目的差不多,比如
{
"name": "@vitepress-code-preview/plugin",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "preview component of code and component in vitepress",
"keywords": ["Vite", "VitePress", "Vue", "plugin", "demo", "preview", "JSX", "TSX"],
"author": "welives",
"license": "MIT",
"type": "module",
"main": "./dist/index.cjs",
"module": "./dist/index.js",
"types": "./dist/index.d.ts",
"exports": {
".": {
"import": "./dist/index.js",
"require": "./dist/index.cjs"
}
},
"files": ["dist", "README.md", "CHANGELOG.md", "package.json", "LICENSE"],
"scripts": {
"dev": "rollup -c --watch",
"build": "rollup -c"
},
"homepage": "https://github.com/welives/vitepress-code-preview",
"repository": {
"type": "git",
"url": "git@github.com:welives/vitepress-code-preview.git"
}
}执行plugin项目的打包脚本pnpm build,不出意外的话应该是打包成功的
测试构建产物
编辑docs/package.json,在生产依赖dependencies添加如下内容,然后执行一下pnpm install,否则docs项目中的node_modules就拿不到构建产物
{
"dependencies": {
"@vitepress-code-preview/container": "workspace:*",
"@vitepress-code-preview/plugin": "workspace:*"
}
}接着编辑docs/vite.config.ts、docs/.vitepress/config.ts和docs/.vitepress/theme/index.ts,把之前开发时用的相对路径改成子项目的包名
import { viteDemoPreviewPlugin } from '@vitepress-code-preview/plugin'import { demoPreviewPlugin } from '@vitepress-code-preview/plugin'import DemoPreview, { useComponents } from '@vitepress-code-preview/container'
import '@vitepress-code-preview/container/dist/style.css'执行docs项目的pnpm docs:dev启动开发环境进行测试,没问题的话再执行pnpm docs:build打包。打包完成后执行pnpm docs:preview进行预览
预览也没问题的话,就编辑主项目的package.json,添加一些脚本命令,便于直接在主项目调用子项目的脚本
{
"scripts": {
"docs:dev": "pnpm --filter=code-preview-example docs:dev",
"docs:preview": "pnpm --filter=code-preview-example docs:preview",
"docs:build": "pnpm --filter=code-preview-example docs:build",
"build": "pnpm container:build && pnpm plugin:build",
"container:dev": "pnpm --filter=@vitepress-code-preview/container dev",
"container:build": "pnpm --filter=@vitepress-code-preview/container build",
"plugin:dev": "pnpm --filter=@vitepress-code-preview/plugin dev",
"plugin:build": "pnpm --filter=@vitepress-code-preview/plugin build"
}
}发布前准备
准备要发布了,完善一下主项目的package.json,把作者信息、仓库地址、关键字之类的填上
{
"name": "vitepress-code-preview",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "preview component of code and component in vitepress",
"keywords": ["Vite", "VitePress", "Vue", "JSX", "TSX", "demo", "preview"],
"author": "welives",
"license": "MIT",
"homepage": "https://github.com/welives/vitepress-code-preview",
"repository": {
"type": "git",
"url": "git@github.com:welives/vitepress-code-preview.git"
}
// ...
}README拷贝脚本
README 使用文档的编写直接略过
安装 esno ,用来直接执行 TS 脚本文件
pnpm add esno -wD编辑主项目的package.json,添加一个copy脚本命令
{
"scripts": {
// ...
"copy": "esno ./scripts/copy.ts"
}
}在主项目中新建scripts/copy.ts,填入如下内容,作用是把主项目的 README.md 拷贝到要发布 npm 的子项目中
import { copyFileSync } from 'fs'
import { resolve } from 'path'
const getFileAbsolutePath = (path: string) => resolve(__dirname, path)
const copyFile = (copyPath: string, targetPath: string) => copyFileSync(copyPath, targetPath)
export const copyReadmeFile = (targetPaths: string[]) => {
const README_PATH = getFileAbsolutePath('../README.md')
targetPaths.forEach((target: string) => {
copyFile(README_PATH, getFileAbsolutePath(target))
})
}
// 复制README.md文件至所有packages包中
copyReadmeFile(['../packages/container/README.md', '../packages/plugin/README.md'])编辑主项目的tsconfig.json,增加如下include字段
{
"include": ["scripts"]
}管理版本及更新日志
我这里使用的是 @changesets/cli 这个包来进行管理
pnpm add -wD @changesets/cli @changesets/changelog-github
pnpm changeset init编辑.changeset/config.json
{
"$schema": "https://unpkg.com/@changesets/config@3.0.0/schema.json",
"changelog": "@changesets/cli/changelog",
"commit": false,
"fixed": [],
"linked": [["@vitepress-code-preview/container", "@vitepress-code-preview/plugin"]],
"access": "public",
"baseBranch": "main",
"updateInternalDependencies": "patch",
"ignore": [],
"___experimentalUnsafeOptions_WILL_CHANGE_IN_PATCH": {
"onlyUpdatePeerDependentsWhenOutOfRange": true
}
}编辑主项目的package.json,添加如下脚本命令
{
"scripts": {
// ...
"changeset": "changeset",
"changeset-version": "changeset version"
}
}生成日志的步骤:执行pnpm changeset,构建日志信息
- ①首先是让你选择哪些项目需要生成更新信息
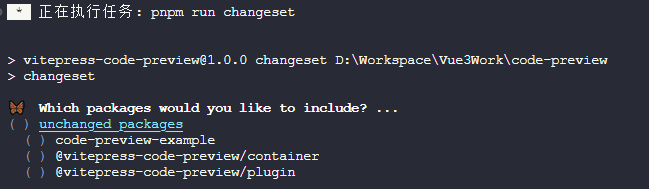
- ②这一步是让你选择哪些项目需要进行
major级别(就是主版本号更新)的更新,如果不需要则按回车跳过
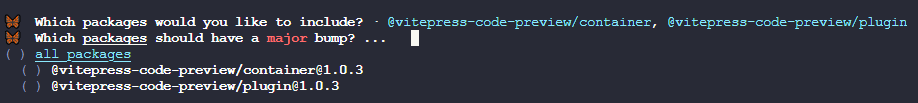
- ③这一步是让你选择哪些项目需要进行
minor级别(就是次版本号更新)的更新,如果不需要则按回车跳过
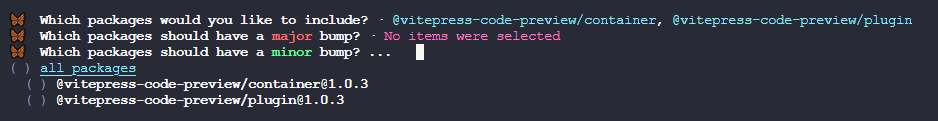
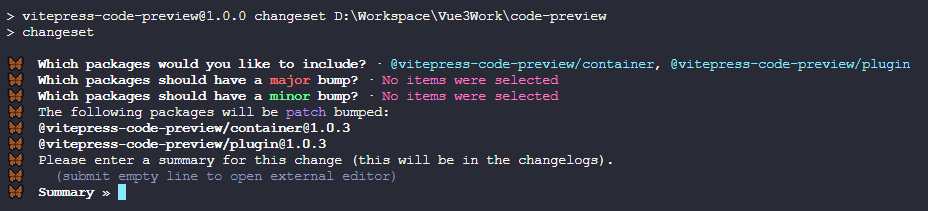
- ④如果前两个选择都跳过了,那么直接就是
patch级别(就是补丁版本号更新)的更新了,会让你输入更新信息
- ⑤最后一步是让你确认操作是否没问题,没问题的话按回车同意会生成更新文件等待应用
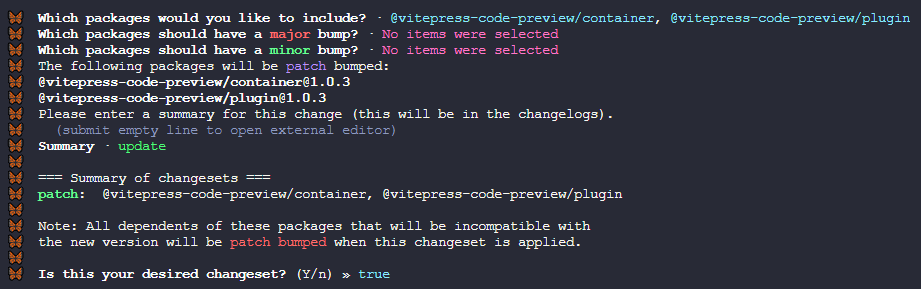
- ⑥执行
pnpm changeset-version应用更新信息
在终端登录npm账号
如果还没有 npm 账号的话,先去注册一个
如果当前不是使用官方源的话,需要先切到官方源 npm config set registry https://registry.npmjs.org
在终端中进入到你要发布的项目目录,执行如下命令
npm login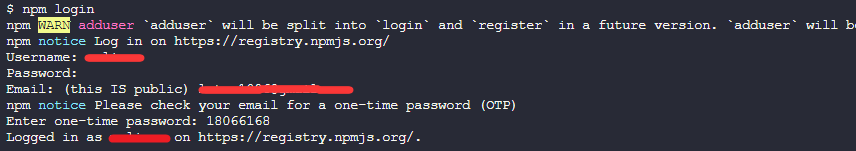
⚡ 提示
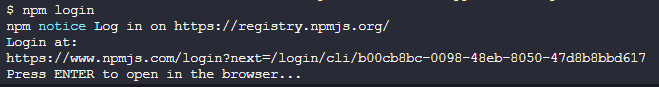
如果提示你打开浏览器进行操作的话,那么需要对 nodejs 进行降级处理,这里以降级到16.19.0版本为例。
因为我是用nvm管理的 nodejs 版本,所以降级命令如下:
nvm install 16.19.0
nvm use 16.19.0发布到npm
发布前记得要先打包
如果要发布的包没带有命名空间(就是包名以@开头的)的话,那么直接执行 pnpm publish 即可
如果带有命名空间的话,那么需要执行 pnpm publish --access public,前提必须要有权限或命名空间真实存在,否则会报错
如果不存在命名空间,你可以自己创建一个。去 npm 官网登录你的账号,在个人设置页可以找到创建入口
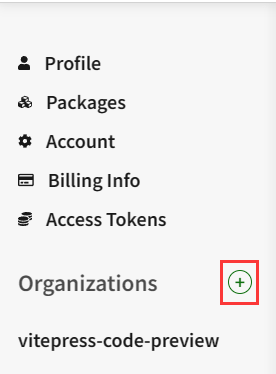
创建完毕后执行pnpm publish --access public
⚡注意
如果想单独发布子项目的话,需要进入到子项目的目录,然后执行pnpm publish --access public
示例项目部署到Github Pages
编辑docs/.vitepress/config.ts,修改base的值为你的 Github 仓库名称,比如我这里是/vitepress-code-preview
// ...
export default defineConfig({
base: '/vitepress-code-preview',
// ...
})主项目新建.github/workflows/deploy-docs.yml,填入如下内容
然后推送main分支代码给 Github 仓库后会自动执行部署
查看
# 工作流名称
name: Build and Deploy Example
# 用于描述工作流的何时触发
on:
workflow_dispatch: {}
push:
branches: [main]
pull_request:
branches:
- main
# 设置GITHUB_TOKEN的权限
permissions:
contents: read
pages: write
id-token: write
# Allow only one concurrent deployment, skipping runs queued between the run in-progress and latest queued.
# However, do NOT cancel in-progress runs as we want to allow these production deployments to complete.
concurrency:
group: pages
cancel-in-progress: false
# 工作流里的任务
jobs:
# 构建
build:
# 指定该任务运行的系统,目前可选的有 ubuntu、windows、和 macOS
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
# 任务里的运行步骤
steps:
# 代码检出
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
fetch-depth: 0
# 安装 Node.js
- name: Install Node.js
uses: actions/setup-node@v4
with:
node-version: 16
# 配置 github pages
- name: Setup Pages
uses: actions/configure-pages@v3
# 安装 pnpm
- name: Install pnpm
uses: pnpm/action-setup@v2
with:
version: 8
run_install: false
# 设置 pnpm 缓存目录
- name: Get pnpm store directory
shell: bash
run: |
echo "STORE_PATH=$(pnpm store path --silent)" >> $GITHUB_ENV
- uses: actions/cache@v3
name: Setup pnpm cache
with:
path: ${{ env.STORE_PATH }}
key: ${{ runner.os }}-pnpm-store-${{ hashFiles('**/pnpm-lock.yaml') }}
restore-keys: |
${{ runner.os }}-pnpm-store-
# 安装依赖
- name: Install dependencies
run: pnpm install --no-frozen-lockfile
# 插件打包
- name: Build plugin
run: pnpm build
# 示例项目打包
- name: Build with VitePress
run: |
pnpm docs:build
touch docs/.vitepress/dist/.nojekyll
# 上传到 Github Pages 部署环境
- name: Upload artifact
uses: actions/upload-pages-artifact@v2
with:
path: docs/.vitepress/dist
# 部署到GitHubPages
deploy:
environment:
name: github-pages
url: ${{ steps.deployment.outputs.page_url }}
needs: build
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
# 部署 GitHub Pages
- name: Deploy to GitHub Pages
id: deployment
uses: actions/deploy-pages@v2🎉 完结撒花

到这里,此笔记就全部结束了,感谢大家的阅读,希望对大家有所帮助。